Recent Publications
![]() Murphy S, Spradlin TR, Mackey B, McVee J and others. 2012. Age estimation, growth and age-related mortality of Mediterranean monk seals Monachus monachus. Endangered Species Research 16:149-163. [PDF 1.4]
Murphy S, Spradlin TR, Mackey B, McVee J and others. 2012. Age estimation, growth and age-related mortality of Mediterranean monk seals Monachus monachus. Endangered Species Research 16:149-163. [PDF 1.4]
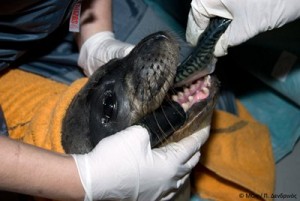
ABSTRACT: Mediterranean monk seals Monachus monachus are classified as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List, with <600 individuals split into 3 isolated sub-populations, the largest in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Canine teeth collected during the last 2 decades from 45 dead monk seals inhabiting Greek waters were processed for age estimation. Ages were best estimated by counting growth layer groups (GLGs) in the cementum adjacent to the root tip using unprocessed longitudinal or transverse sections (360 µm thickness) observed under polarized light. Decalcified and stained thin sections (8 to 23 µm) of both cementum and dentine were inferior to unprocessed sections. From analysing patterns of deposition in the cementum of known age-maturity class individuals, one GLG was found to be deposited annually in M. monachus. Ages ranged from 0.5 to 36 yr for females, 0.5 to 21 yr for males and 0.5 to 25.5 yr for individuals of unknown sex. The majority of seals (65%) were considered adults (≥4 yr), followed by juveniles (20%, <1 yr) and sub-adults (15%, 1−3.9 yr). Thirty percent of the aged sample had died from human-related causes, such as accidental entanglement in fishing gear and direct killings. A single-Gompertz growth curve was generated for both sexes using standard length data, resulting in asymptotic values of 212.3 cm for females and 221.8 cm for males. This study represents the first quantitative glimpse of sex-specific growth in monk seals and the age structure of dead individuals in this rare species’ core range.

 The huge scale of the Costa Concordia disaster is apparent in this satellite image of the stricken cruise ship just off the Italian island of Giglio.
The huge scale of the Costa Concordia disaster is apparent in this satellite image of the stricken cruise ship just off the Italian island of Giglio. The Aquatic Mammals special edition on Mediterranean and Hawaiian monk seals, whose publication was announced with some excitement in September last year, has finally been made available for public purchase. As far as we can ascertain, those unlucky enough not to have institutional access or public libraries with AA subscriptions, will be paying $12 for each paper they choose to purchase. One author, Giulia Mo (listed below) has, however, asked us to inform interested readers that she will email copies of her paper free of charge to those who request it. Please contact:
The Aquatic Mammals special edition on Mediterranean and Hawaiian monk seals, whose publication was announced with some excitement in September last year, has finally been made available for public purchase. As far as we can ascertain, those unlucky enough not to have institutional access or public libraries with AA subscriptions, will be paying $12 for each paper they choose to purchase. One author, Giulia Mo (listed below) has, however, asked us to inform interested readers that she will email copies of her paper free of charge to those who request it. Please contact: